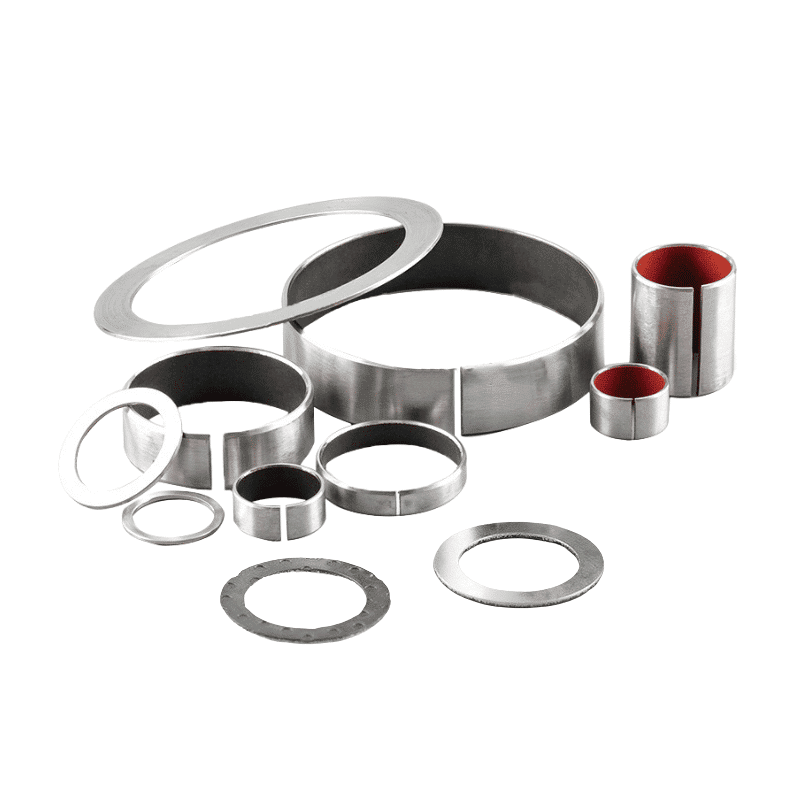
Self-lubricating thrust bearing washer
Bearings and Bushings for the Future: Precision and Customization: Our company, in bearing engineering with decades of experience, designs and develops high-precision self-lubricating bronze bearings & plain bushes. We offer a wide array of sliding bearings tailored to meet specific needs. Renowned for our expertise in custom bronze bushing and slide plate solutions, we provide an expansive selection of bushing metal alloys. Contact us today to benefit from unparalleled services at competitive prices.
Self-lubricating thrust bearing washer
self-lubricating thrust bearing washer
Self-lubricating thrust bearing washers are designed to provide low friction and maintenance-free operation in various applications. They are typically made of materials that can withstand high loads while minimizing wear and tear. To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it is essential to measure the clearance between the bearing washer and its mating components. This clearance plays a vital role in the proper functioning of the thrust bearing assembly.
polymer-based bearings
Thrust Washer
innovative polymer-based bearings and offers a range of self-lubricating thrust washer bearings suitable for different applications and industries.
professional
Thrust Washer
Well-established manufacturer of bearings, including self-lubricating thrust washer bearings. They serve various industries, including defense, and industrial markets.
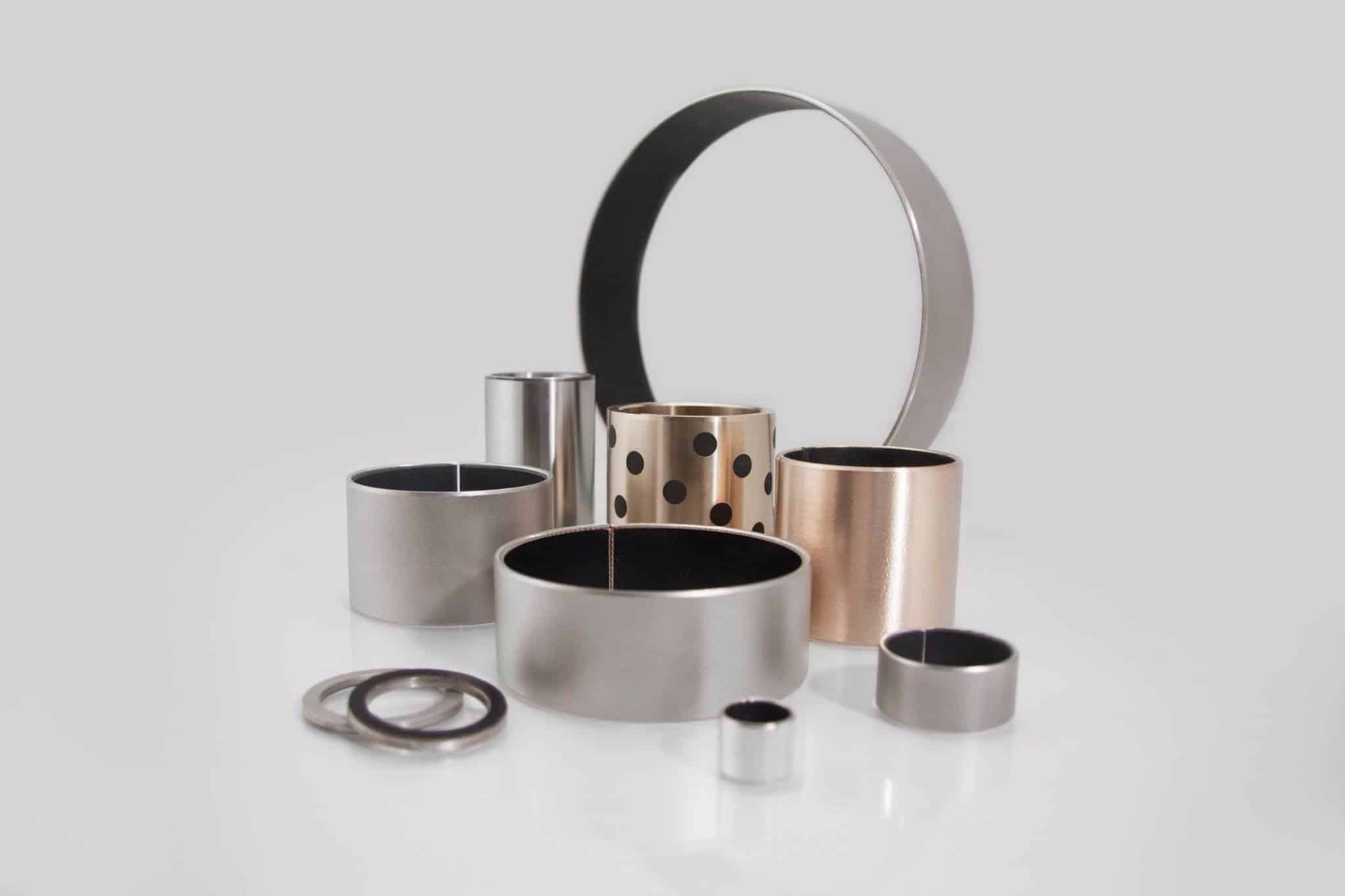
Metal Bearing
Focus
Global manufacturer of slide bearing and bushings, offering a variety of self-lubricating thrust washer bearings for different applications.
Custom Size
Self-lubricating Bearing washer
Custom-made self-lubricating thrust washer bearings. These companies can provide tailored solutions based on your specific requirements, such as size, load capacity, and material.
Self-Lubricating Thrust Bearing Washer
A self-lubricating thrust bearing washer is a type of bearing designed to manage axial loads in various applications with minimal friction and wear. It consists of a metal backing and a self-lubricating layer that provides a low-friction, wear-resistant surface, reducing the need for external lubrication. These bearings are commonly used in applications where space constraints, maintenance reduction, and weight savings are essential.
When selecting a self-lubricating thrust bearing washer, it is essential to consider factors such as load capacity, operating temperature, speed, and environmental conditions. Ensure that the chosen bearing is appropriate for your specific application and meets the required performance criteria. Regular inspection and monitoring of the bearing’s condition can help optimize its performance and extend its service life.
taxation planning
Eiusmod tempor incididunt ipsum ut labore dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim minim veniam duisy ipsum sed quis.

self-lubricating Metal bearing washer
We offers a wide range of self-lubricating bearings, including thrust washer bearings. we provide solutions for various applications and industries.
Specializes in high-performance, self-lubricating bearings, including thrust washer bearings in various industries such as automotive and industrial equipment.
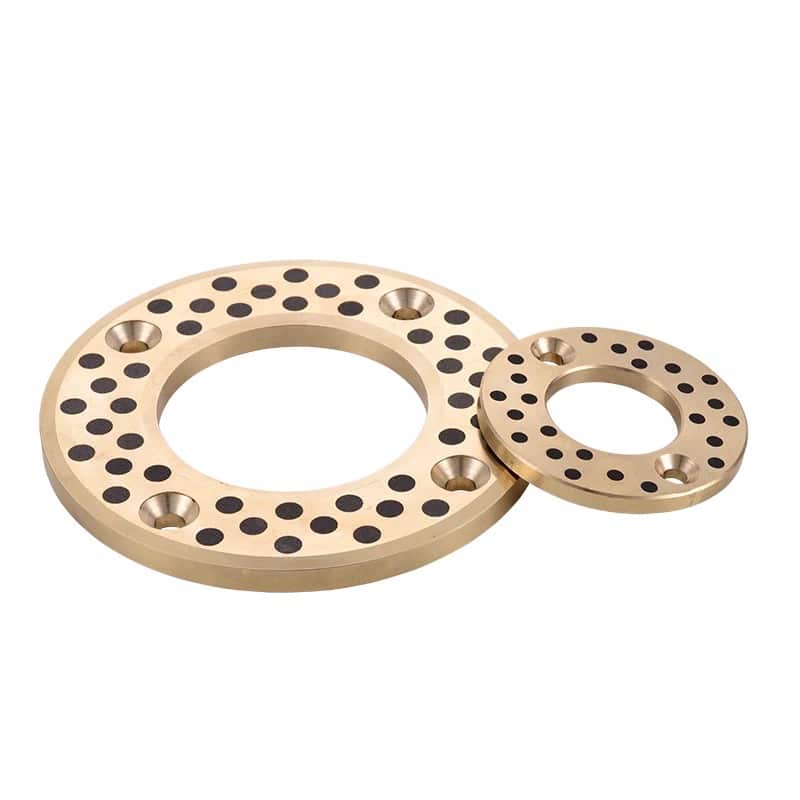
Oilless graphite bronze thrust bearings
Oilless graphite bronze thrust bearings are designed to operate without additional lubrication due to the self-lubricating properties of the graphite embedded in the bronze material. However, in some cases, adding extra lubrication may be beneficial, especially during the initial start-up or in harsh environments.
Oilless graphite thrust washer bearings are designed to support axial loads without the need for external lubrication. These bearings consist of a metal backing, usually made of materials like bronze, steel, or other alloys, and are embedded with solid lubricant graphite plugs. The graphite serves as a self-lubricating agent, reducing friction and wear during operation.

We Deliver Metal Thrust Washer At Your Address
Here’s how to grease an oilless graphite bronze
thrust Bearing:

How do you grease a thrust bearing?
Choose the right grease: Select a grease that is compatible with the bronze material and graphite. Typically, a high-quality lithium-based or calcium-based grease with EP (extreme pressure) additives is suitable for bronze bearings.
Clean the bearing and application area: Before applying the grease, ensure that the bearing and surrounding components are clean and free from dirt, debris, or old lubricant.
Apply grease to the bearing surfaces: Using a grease gun, apply a thin layer of grease to the bearing surfaces, including the graphite-infused areas. Make sure to cover the entire surface of the bearing uniformly. Be cautious not to over-lubricate, as excessive grease can cause increased friction and generate heat.
Assemble the bearing components: Reassemble the thrust bearing and its mating components, ensuring that they are properly aligned and seated.
Wipe away excess grease: Use a clean cloth or wipe to remove any excess grease from the bearing and its surrounding components.
Monitor the bearing: After greasing the oilless graphite bronze thrust bearing, monitor its performance to ensure that the added lubrication does not cause any issues, such as overheating or excessive friction.
It is important to note that oilless graphite bronze thrust bearings are designed to operate with minimal maintenance and typically do not require additional lubrication. However, adding grease in specific circumstances can help to improve the bearing’s performance and lifespan. Always consult the bearing manufacturer’s guidelines for proper maintenance procedures and recommendations.
Graphite self-lubricating thrust washer supplier
What does a thrust Bearing Do On A Washing Machine?
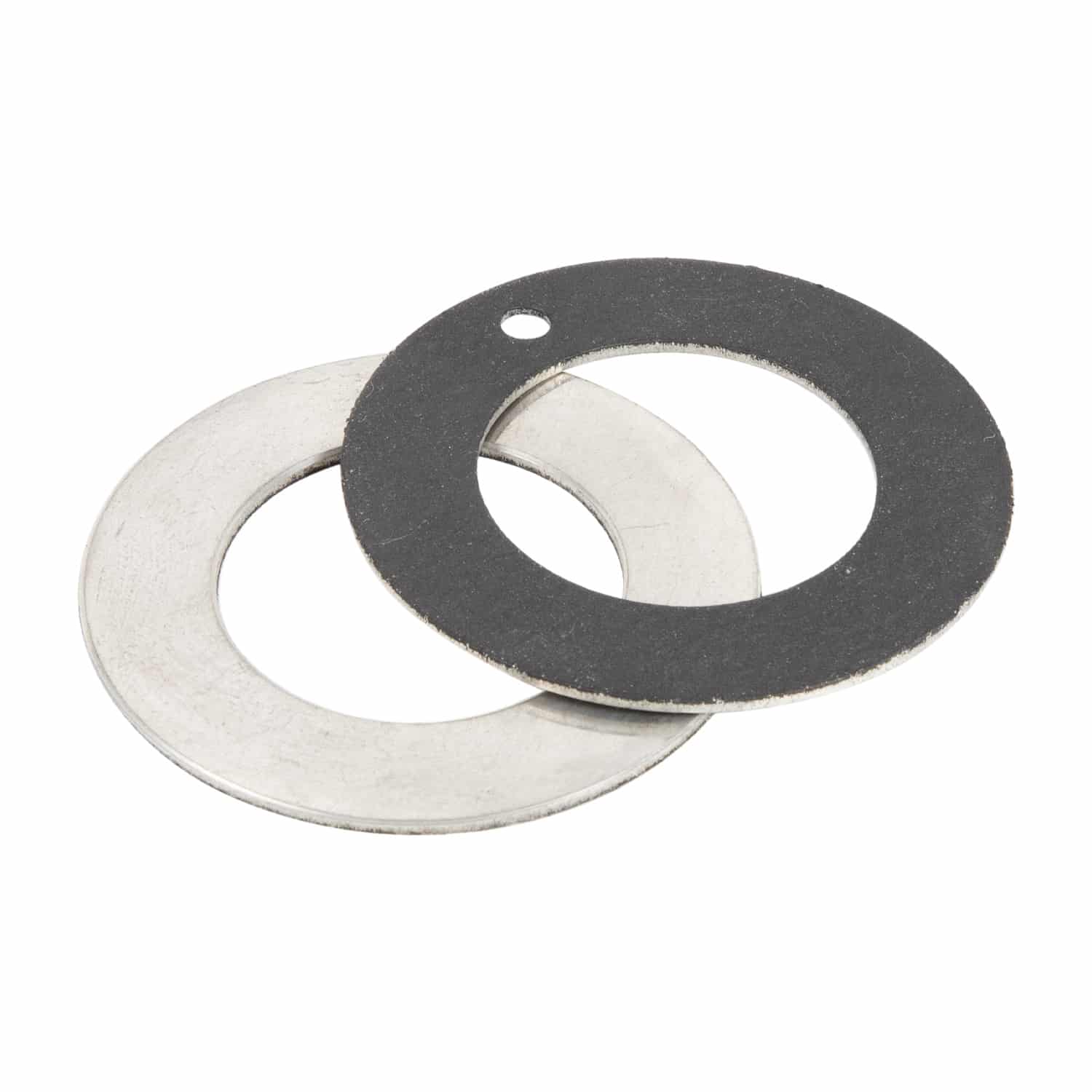

A steel PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) thrust bearing in a washing machine serves as a low-friction, wear-resistant component that supports and manages axial loads generated during the operation of the machine. The primary function of the thrust bearing is to allow smooth rotation of the washer’s drum or agitator while maintaining proper alignment and minimizing wear on other components.
Steel PTFE thrust bearings are particularly suitable for washing machines due to their self-lubricating properties, which reduce the need for maintenance and additional lubrication. The PTFE lining on the steel bearing reduces friction and wear, allowing the washer to operate more efficiently and prolonging the lifespan of the bearing and other components.
In a washing machine, the steel PTFE thrust bearing is typically located between the main shaft and a supporting component, such as the drum’s support structure or the agitator’s base. When the machine is in operation, the thrust bearing accommodates the axial forces generated by the rotation and movement of the drum or agitator, ensuring smooth and reliable performance.
In summary, a steel PTFE thrust bearing in a washing machine plays a crucial role in managing axial loads, reducing friction, and prolonging the life of the machine’s components. Its self-lubricating properties make it an ideal choice for washing machines, where low maintenance and reliable operation are essential.
Self-lubricating steel ptfe washer supplier
How to Install crankshaft bronze thrust Bearing?
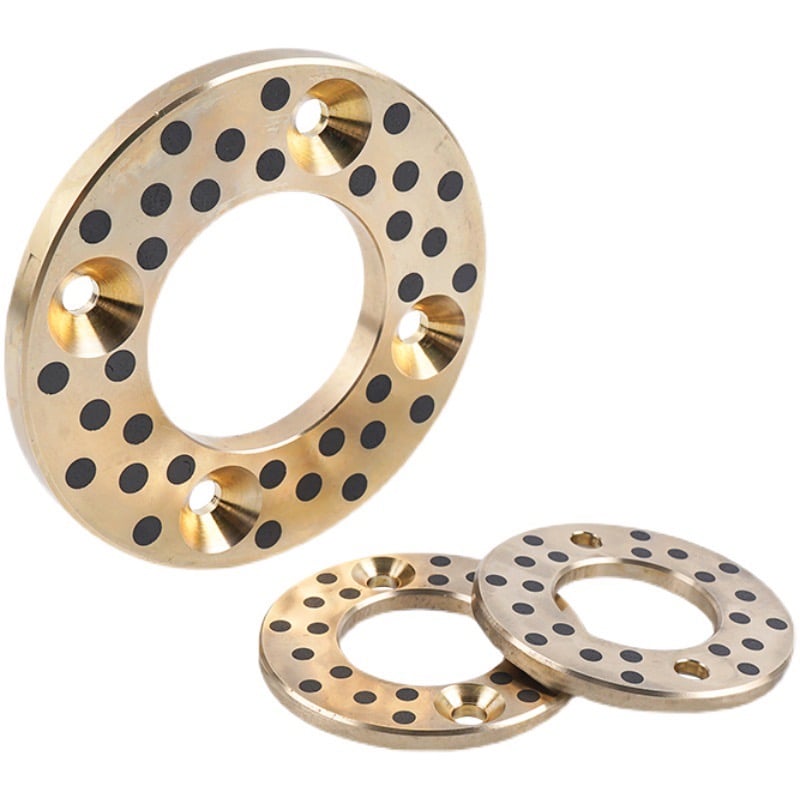

Installing crankshaft bronze thrust bearings is a critical process that requires attention to detail and proper procedures to ensure the correct fit and function of the engine. The following steps outline the general process of installing bronze thrust bearings in a crankshaft:
Prepare the components: Before starting, ensure that all engine components, including the crankshaft, engine block, and bearing surfaces, are clean and free of debris or contaminants. Inspect the components for any signs of damage or wear that might interfere with the installation or performance of the thrust bearings.
Measure bearing clearances: Using a micrometer or plastigauge, measure the clearances between the crankshaft journals and the main bearing saddles in the engine block. Compare these measurements with the manufacturer’s specifications to ensure that the clearances are within the acceptable range. Make any necessary adjustments or replacements to achieve the proper clearances.
Lubricate the thrust bearings: Apply a generous amount of assembly lube or engine oil to both the bearing surfaces and the crankshaft journals to ensure proper lubrication during installation and initial start-up.
Install the thrust bearings: Position the bronze thrust bearings in their designated location on the engine block, ensuring that the bearing’s locating tangs align with the corresponding grooves in the block. Some engines may have the thrust bearings integrated into the main bearing shells, in which case you should install the main bearings with the thrust bearing surfaces in the correct orientation.
Install the crankshaft: Carefully lower the crankshaft into the engine block, making sure that it rests evenly on the bearing surfaces without damaging the thrust bearings.
Install the main bearing caps: Position the main bearing caps (including the cap with the other half of the thrust bearings, if applicable) onto the engine block, ensuring that they are correctly oriented and aligned. Apply assembly lube or engine oil to the bearing surfaces and crankshaft journals before installing the caps.
Torque the main bearing cap bolts: Tighten the main bearing cap bolts in a staggered pattern and in stages, following the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications and tightening sequence. This will ensure even clamping force and prevent distortion of the bearing surfaces.
Check thrust bearing clearances: Once the thrust bearings are installed, verify that there is adequate clearance for axial movement (endplay) of the crankshaft. You can use a dial indicator or feeler gauge to measure the endplay, comparing the measurement to the manufacturer’s specifications. If the endplay is outside the acceptable range, you may need to replace the thrust bearings with a different size or adjust the bearing’s position to achieve the correct clearance.
Reassemble the engine: With the crankshaft and thrust bearings properly installed, proceed to reassemble the rest of the engine components according to the manufacturer’s instructions. This may include installing the connecting rods, pistons, cylinder head, and other related parts.
By following these steps and adhering to the manufacturer’s guidelines, you can successfully install bronze thrust bearings in a crankshaft, ensuring proper fit and reliable engine performance.
Self-lubricating bronze thrust washer supplier
How does a metal polymer thrust Bearing Washer Work In A Gearbox?
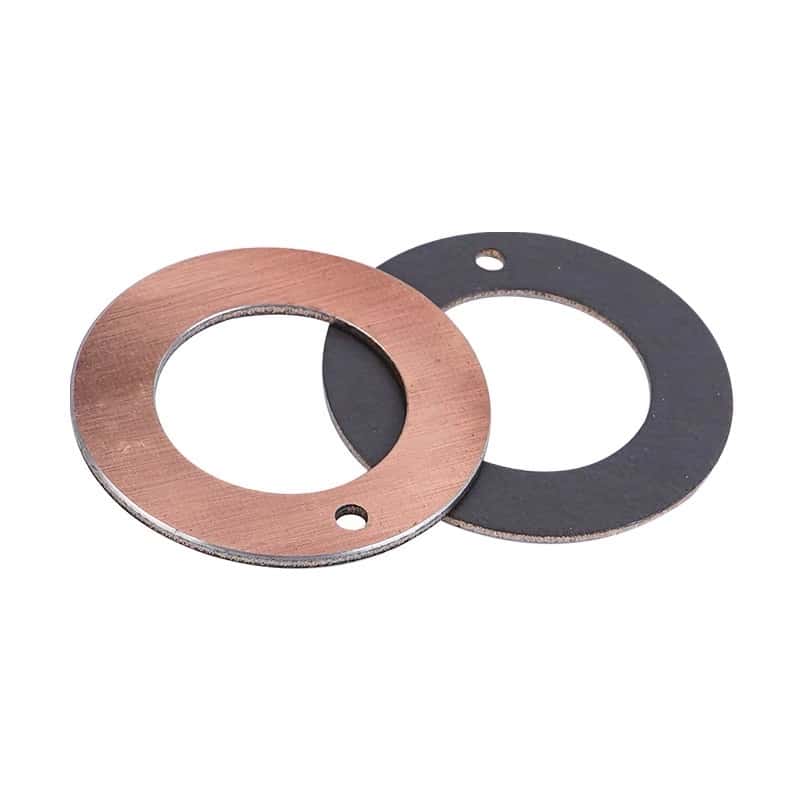

A metal-polymer thrust bearing washer is a type of bearing specifically designed to support axial loads in a gearbox. It consists of a metal backing with a thin polymer layer that provides a low-friction, wear-resistant surface. This unique design offers a combination of the strength and durability of the metal and the self-lubricating properties of the polymer.
In a gearbox, metal-polymer thrust bearing washers play a crucial role in managing axial loads generated during the operation of gears and shafts, ensuring smooth and efficient performance. Here’s how they work:
Load support: When the gears and shafts in a gearbox transmit power, they generate axial forces that need to be supported and managed. Metal-polymer thrust bearing washers are designed to withstand these axial loads, allowing the gearbox components to function effectively without excessive wear or damage.
Low friction: The polymer layer on the bearing washer provides a self-lubricating surface, reducing friction between the bearing and the mating components. This low-friction characteristic ensures smooth operation and minimizes energy loss during the power transmission process.
Wear resistance: The combination of the metal backing and the polymer layer offers excellent wear resistance, prolonging the life of the thrust bearing washer and other gearbox components. The polymer layer also helps to minimize the impact of potential misalignment or surface irregularities, further reducing wear and tear.
Space-saving design: Metal-polymer thrust bearing washers are thin and lightweight, making them ideal for use in gearbox applications where space is limited, and weight reduction is desirable.
Low maintenance: The self-lubricating properties of the polymer layer reduce the need for additional lubrication or maintenance, making metal-polymer thrust bearing washers a reliable and low-maintenance option for gearbox applications.
In summary, metal-polymer thrust bearing washers work in a gearbox by supporting axial loads, reducing friction, and minimizing wear between mating components. Their unique design offers a combination of strength, durability, and self-lubrication, making them an effective and reliable solution for managing axial loads in gearboxes.
Self-lubricating PTFE thrust washer supplier

Solutions For Every Industry
Searching for Dependable Bushing Solutions? viiplus Has What You Need.

Design Guides, Materials
Bushing design, Comprehensive design manuals covering a range of self-lubricating materials used in all of viiplus’s manufacturing processes.

Technical Guides
Manufacturing On Demand, Technical Guides For Machining Design. Discover the latest in metal alloys, materials, and design tips for manufacturing custom machined and self-lubricating bearing parts.

Get Instant Quote
To receive your instant quote, simply upload your drawing file and choose your production process & bushing material.
Prototyping, Place Order
After you place your order, we will start the production process. You will receive updates when your order has completed production and is ready to be dispatched.

Receive Your custom Parts
We provide precision-inspected high-quality parts, packing lists and documents, and delivery tracking.


