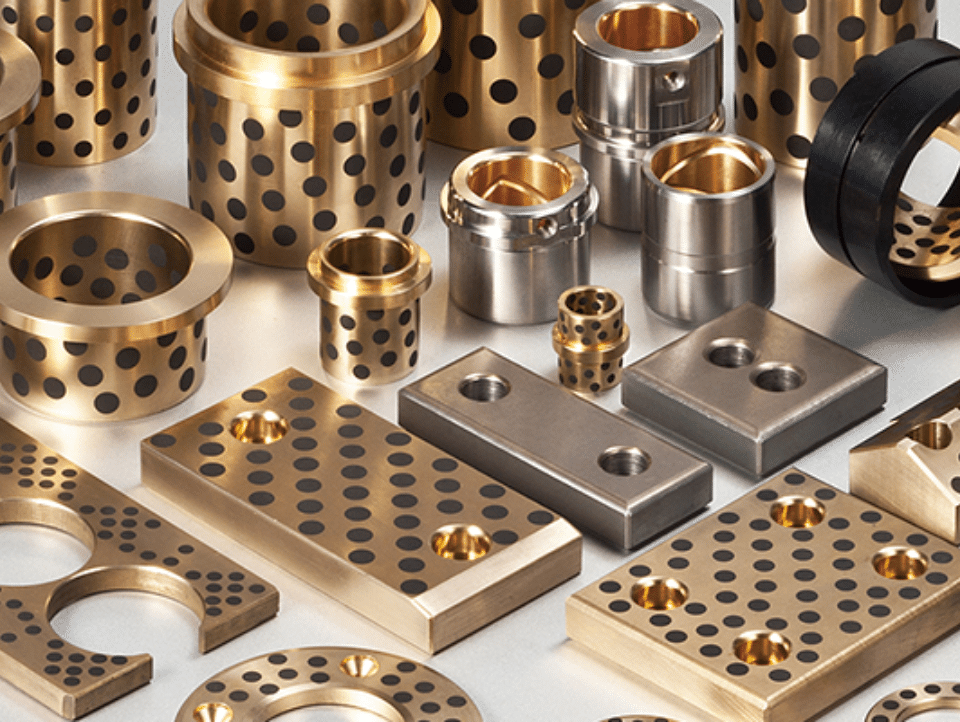

High Tensile Brass CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1
High Tensile Brass CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 Bushing Bearing, we supply high-quality, custom-sized CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 bronze bearing bushes with grooves using CNC machining.
CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 bronze bearing bushes, is a type of high tensile brass known for its exceptional hardness and suitability for demanding machine elements. Below is a detailed breakdown of its properties and characteristics based on the provided information:
Chemical Composition (ASTM B505 C86200)
Element
% Min
% Max
Cu (Copper)
55.0
66.0
Sn (Tin)
–
0.3
Pb (Lead)
–
0.3
Zn (Zinc)
–
Remainder
P (Phosphorus)
–
0.03
Fe (Iron)
0.5
2.5
Ni (Nickel)
–
3.0
Si (Silicon)
–
0.1
Al (Aluminum)
1.0
3.0
Mn (Manganese)
1.0
4.0
Sb (Antimony)
–
0.05
Mechanical Properties (Minimum Values)
Property
Value
Tensile Strength (Rm)
620 MPa
Yield Point (Rp0.2)
260 MPa
Elongation (5D, A)
14%
Hardness (HBw 10-1000)
150
Physical Properties
Property
Value
Density
7.8 kg/dm³
Specific Heat
0.373 J/(g·K)
Thermal Expansion
20.0 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹
Thermal Conductivity
55 – 59 W/(m·K)
Electrical Conductivity
7 – 8 MS/m
Key Features and Applications
- Extreme Hardness: This material is exceptionally hard, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
- High Tensile Strength: With a tensile strength of 620 MPa, it can withstand significant mechanical loads.
- Wear Resistance: Suitable for bearing bushes and other components subjected to friction and wear.
- Machinability: Despite its hardness, it can be machined into precise components.
- Corrosion Resistance: The alloy’s composition provides good resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
Applications
- Bearing Bushes: Used in heavy machinery and automotive applications.
- Machine Elements: Suitable for gears, valves, and other high-demand components.
- Industrial Components: Used in pumps, compressors, and other equipment requiring high strength and durability.
International Standard
The closest international standard for this material is ASTM B505 C86200, which specifies the chemical composition and mechanical properties of high tensile brass alloys.
This material is an excellent choice for applications requiring high strength, hardness, and wear resistance, particularly in demanding industrial environments.
CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 bronze bearing bushes, is a type of high tensile brass known for its exceptional hardness and suitability for demanding machine elements. Below is a detailed breakdown of its properties and characteristics based on the provided information:
Chemical Composition (ASTM B505 C86200)
| Element | % Min | % Max |
|---|---|---|
| Cu (Copper) | 55.0 | 66.0 |
| Sn (Tin) | – | 0.3 |
| Pb (Lead) | – | 0.3 |
| Zn (Zinc) | – | Remainder |
| P (Phosphorus) | – | 0.03 |
| Fe (Iron) | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| Ni (Nickel) | – | 3.0 |
| Si (Silicon) | – | 0.1 |
| Al (Aluminum) | 1.0 | 3.0 |
| Mn (Manganese) | 1.0 | 4.0 |
| Sb (Antimony) | – | 0.05 |
Mechanical Properties (Minimum Values)
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (Rm) | 620 MPa |
| Yield Point (Rp0.2) | 260 MPa |
| Elongation (5D, A) | 14% |
| Hardness (HBw 10-1000) | 150 |
Physical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 7.8 kg/dm³ |
| Specific Heat | 0.373 J/(g·K) |
| Thermal Expansion | 20.0 × 10⁻⁶ K⁻¹ |
| Thermal Conductivity | 55 – 59 W/(m·K) |
| Electrical Conductivity | 7 – 8 MS/m |
Key Features and Applications
- Extreme Hardness: This material is exceptionally hard, making it ideal for high-stress applications.
- High Tensile Strength: With a tensile strength of 620 MPa, it can withstand significant mechanical loads.
- Wear Resistance: Suitable for bearing bushes and other components subjected to friction and wear.
- Machinability: Despite its hardness, it can be machined into precise components.
- Corrosion Resistance: The alloy’s composition provides good resistance to corrosion, especially in harsh environments.
Applications
- Bearing Bushes: Used in heavy machinery and automotive applications.
- Machine Elements: Suitable for gears, valves, and other high-demand components.
- Industrial Components: Used in pumps, compressors, and other equipment requiring high strength and durability.
International Standard
The closest international standard for this material is ASTM B505 C86200, which specifies the chemical composition and mechanical properties of high tensile brass alloys.
This material is an excellent choice for applications requiring high strength, hardness, and wear resistance, particularly in demanding industrial environments.
High-tensile brass bearing CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 bushing
CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 is a type of bronze alloy commonly used for bearing bushes due to its excellent wear resistance, strength, and corrosion resistance. When manufacturing custom-sized bronze bearing bushes with grooves using CNC machining, here are the key steps and considerations:
1. Material Preparation
-
Ensure the CuZn34Mn3Al2Fe1 bronze material is of high quality and meets the required specifications.
-
Cut the raw material to the approximate size needed for the bearing bush.
2. CNC Machining Process
a. Turning
-
Use a CNC lathe to machine the outer diameter (OD) and inner diameter (ID) of the bearing bush to the required dimensions.
-
Ensure the surface finish is smooth to minimize friction during operation.
b. Groove Cutting
-
Program the CNC machine to cut custom grooves on the inner or outer surface of the bush, depending on the application.
-
Grooves can be spiral, straight, or custom-designed to improve lubrication and heat dissipation.
c. Drilling and Boring
-
Drill oil holes or lubrication channels if required.
-
Perform precision boring to achieve the exact inner diameter tolerance.
d. Finishing
-
Deburr and polish the bearing bush to remove sharp edges and improve surface quality.
-
Apply any additional surface treatments, such as coating or heat treatment, if necessary.
3. Quality Control
-
Measure the dimensions of the bearing bush using precision tools like micrometers, calipers, or CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine).
-
Check the surface finish and groove geometry to ensure they meet the design specifications.
-
Perform functional tests, such as fit checks with the shaft, to ensure proper operation.
4. Customization Considerations
-
Size: Provide exact dimensions (OD, ID, length) and tolerances for the custom bearing bush.
-
Groove Design: Specify the type, depth, width, and pattern of the grooves.
-
Lubrication Requirements: Include details about oil holes or channels if needed.
-
Application: Consider the operating conditions (load, speed, temperature) to ensure the material and design are suitable.
5. CNC Programming
-
Use CAD/CAM software to create a 3D model of the bearing bush and generate the CNC machining program.
-
Optimize the toolpath to minimize machining time and ensure precision.
6. Packaging and Delivery
-
Pack the finished bearing bushes securely to prevent damage during transportation.
-
Label the parts with relevant information (material, size, part number) for easy identification.




