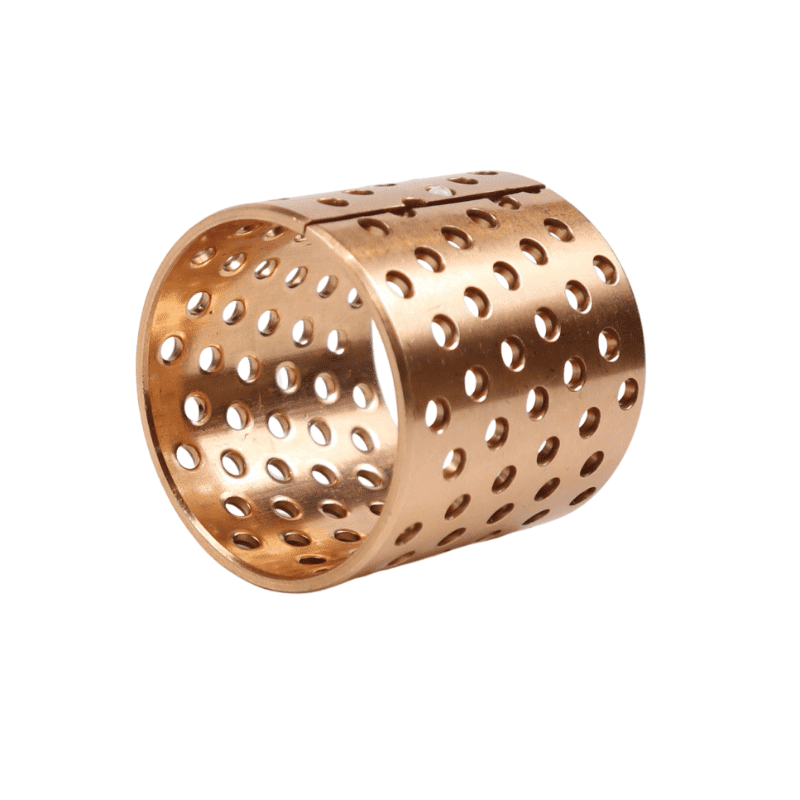
Tin Bronze Sleeves
Tin Bronze Sleeves
Say goodbye to the hassle of frequent lubrication maintenance. Our self-lubricating technology ensures smooth operation and reduces wear and tear, extending the lifespan of your equipment. Experience uninterrupted productivity and cost savings as you bid farewell to the need for messy lubricants and time-consuming upkeep.
Manufacturing on Demand, alternative solutions
Tin Bronze Sleeves
Various copper alloy materials, particularly those used in copper sleeves, we need to focus on several key types: Tin Bronze Sleeves, Aluminum Bronze Sleeves, and Phosphor Bronze Sleeves, including specific grades like QSn10-1, QSn10-2, QA110-4-4, QSn7-0.2, and QSn10-10.
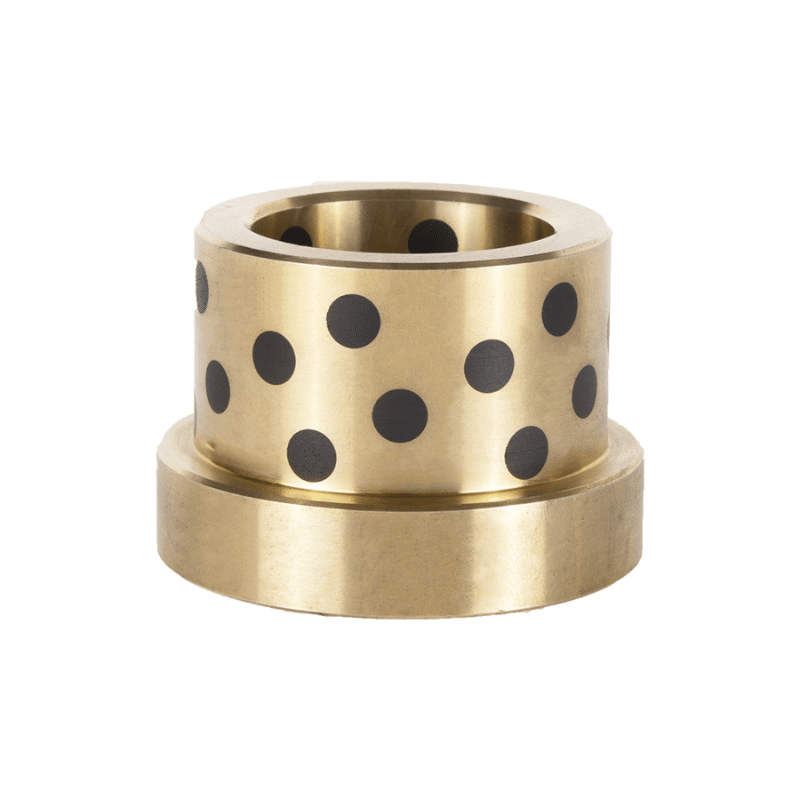
The unique combination of material composition and self-lubricating properties makes tin bronze sleeves an excellent choice for various mechanical applications. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions while minimizing maintenance requirements is highly valued in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing.
Tin bronze sleeves are a popular choice in various industrial applications due to their unique material composition and self-lubricating properties.
Tin Bronze Sleeves
Introduction
- Briefly introduce copper alloys and their importance in various industries.
- Mention the focus on copper sleeves and their applications.
Tin Bronze Sleeves (QSn10-1, QSn10-2)
- Describe tin bronze alloys, focusing on QSn10-1 and QSn10-2 grades.
- Discuss their properties such as high wear resistance, good mechanical properties, and resistance to corrosion.
- Highlight common applications like bearings, gears, and valve components.
Aluminum Bronze Sleeves (QA110-4-4)
- Explain the composition and characteristics of aluminum bronze, with a focus on the QA110-4-4 grade.
- Emphasize its high strength, excellent corrosion resistance, and suitability for heavy-duty applications.
- Mention typical uses in aerospace, marine, and heavy machinery.
Phosphor Bronze Sleeves (QSn7-0.2, QSn10-10)
- Detail phosphor bronze, particularly grades QSn7-0.2 and QSn10-10.
- Cover their features such as excellent fatigue and wear resistance, and good conductivity.
- Discuss applications in electrical components, springs, and fasteners.
Comparison and Selection
- Compare the properties of tin, aluminum, and phosphor bronze alloys.
- Provide guidance on selecting the right material based on application requirements.
When discussing tin bronze sleeves, particularly focusing on the materials QSn10-1, QSn10-2, QA110-4-4, QSn7-0.2, and QSn10-10, it’s important to understand their composition, properties, and typical applications. Here’s a detailed look at each:
1. QSn10-1 (Tin Bronze)
- Composition: This material is primarily a tin bronze alloy, with about 10% tin and a small percentage of phosphorous for added strength and corrosion resistance.
- Properties: QSn10-1 is known for its excellent wear resistance, good mechanical properties, and resistance to corrosion. It has a good combination of strength and ductility.
- Applications: It is commonly used in manufacturing bearings, gears, and valve components, especially where resistance to fatigue and wear is crucial.
2. QSn10-2 (Tin Bronze)
- Composition: Similar to QSn10-1, this alloy also contains about 10% tin. The slight variation in composition impacts its mechanical properties slightly.
- Properties: QSn10-2 offers high fatigue resistance, good load-bearing qualities, and resistance to wear and corrosion. It’s slightly more ductile than QSn10-1.
- Applications: Ideal for heavy-duty bearings, worm wheels, and other components requiring high durability under load.
3. QA110-4-4 (Aluminum Bronze)
- Composition: This is an aluminum bronze alloy, distinct from tin bronzes. It typically contains aluminum, iron, and nickel in its composition.
- Properties: QA110-4-4 is known for its high strength and excellent corrosion resistance, especially in seawater and brine environments. It also has good wear resistance.
- Applications: Frequently used in marine applications, aerospace, and heavy machinery components due to its strength and corrosion resistance.
4. QSn7-0.2 (Phosphor Bronze)
- Composition: This phosphor bronze contains around 7% tin and a small amount of phosphorous.
- Properties: It’s recognized for its fine grain, good fatigue resistance, and excellent formability. It also has good corrosion resistance.
- Applications: Commonly used in electrical connectors, springs, and fasteners, where good electrical conductivity and fatigue resistance are required.
5. QSn10-10 (Phosphor Bronze)
- Composition: A higher tin content phosphor bronze, with about 10% tin.
- Properties: This alloy offers high wear resistance, good mechanical strength, and excellent corrosion resistance. It also has good elasticity.
- Applications: Ideal for high-strength electrical components, springs, and bearing parts where high resistance to fatigue, wear, and corrosion is needed.
In summary, these materials are specifically tailored for applications requiring high strength, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance. The choice among these alloys depends on the specific requirements of the application, including environmental conditions, mechanical stress, and the desired lifespan of the component.
- Summarize the key points about these copper alloys.
- Highlight their critical role in various industrial applications.
Tin bronze sleeves are a popular choice in various industrial applications due to their unique material composition and self-lubricating properties. Here’s an overview of these aspects:
Material Composition of Tin Bronze Sleeves
- Primary Element: Tin – The principal component of tin bronze is tin, typically ranging from 5% to 12%. This high tin content significantly enhances the alloy’s strength and corrosion resistance.
- Copper Base: The majority of the alloy is copper, contributing to its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to corrosion.
- Additives: Small amounts of other elements like phosphorus, zinc, or lead may be added. Phosphorus increases wear resistance and stiffness, while lead improves machinability and can contribute to the alloy’s self-lubricating properties.
Self-Lubricating Properties
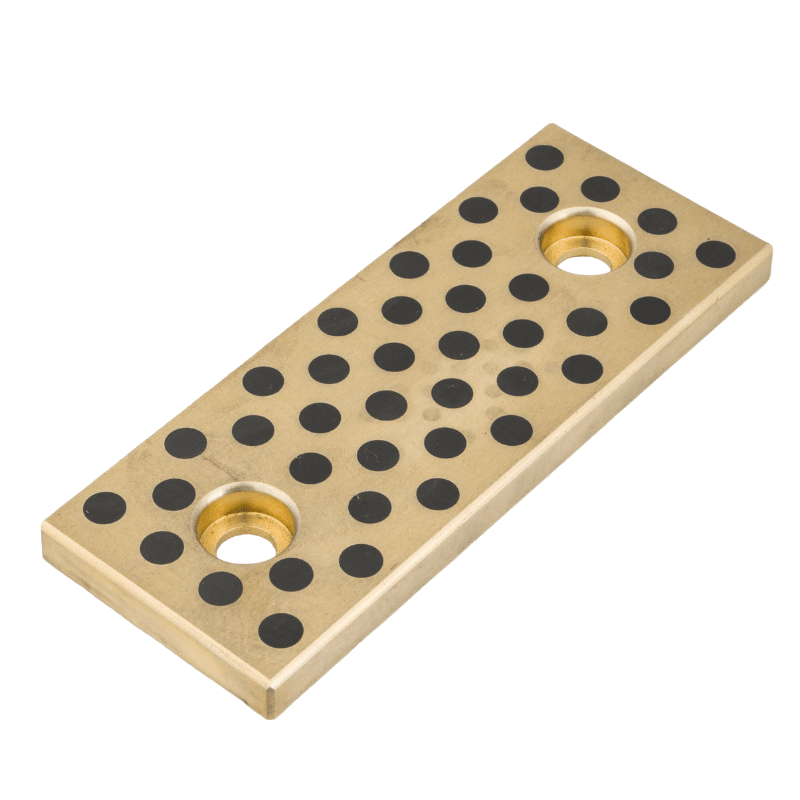
- Lead Inclusions: In some tin bronze alloys, lead is added to enhance self-lubricating properties. Lead does not alloy with copper and tin but is present in microscopic pockets within the metal. Under friction, these pockets provide a lubricating effect, reducing wear and tear on both the sleeve and the mating surface.
- Porosity for Lubricant Retention: Some tin bronze sleeves are designed with a porous structure. These pores can be impregnated with lubricants, which are then released under operational conditions, providing consistent lubrication over time.
- Surface Treatments: Surface treatments or coatings can also be applied to tin bronze sleeves to enhance their self-lubricating capabilities. These might include films or layers of materials that reduce friction and wear.
Applications
Due to their composition and self-lubricating features, tin bronze sleeves are ideal for applications where durability and reduced maintenance are key. They are commonly used in:
- Bearings and Bushings: Especially in heavy machinery and automotive applications where they mitigate wear under high-load and high-speed conditions.
- Valve Components: Where their corrosion resistance and self-lubricating properties ensure smooth operation over long periods.
- Gear Components: In scenarios where robustness against wear and corrosion is critical.
Your expert in self-lubricating Bearing
and Bronze alloys – serving globally
Brand replacement products and functionally equivalent parts, alternative solutions
Manufactures flange bronze bearings, service & maintenance companies to meet the exacting specifications required in a wide range of industrial applications.
Machined bronze bushing that meet the exacting requirements & specifications supplied by our clients. Spherical bearings, spindles, semi-spheres and supports that we have manufactured.
You will find to follow a selection of self lubricating bronze bearing material CuSn7Zn4Pb7, CuSn12, CuAl10Fe5Ni5,
CuZn25Al5Mn4Fe3
Alternative solution,We offer an outsourced machining service for bronze bushes, manufacturing precise parts to the designs supplied to us by our clients.
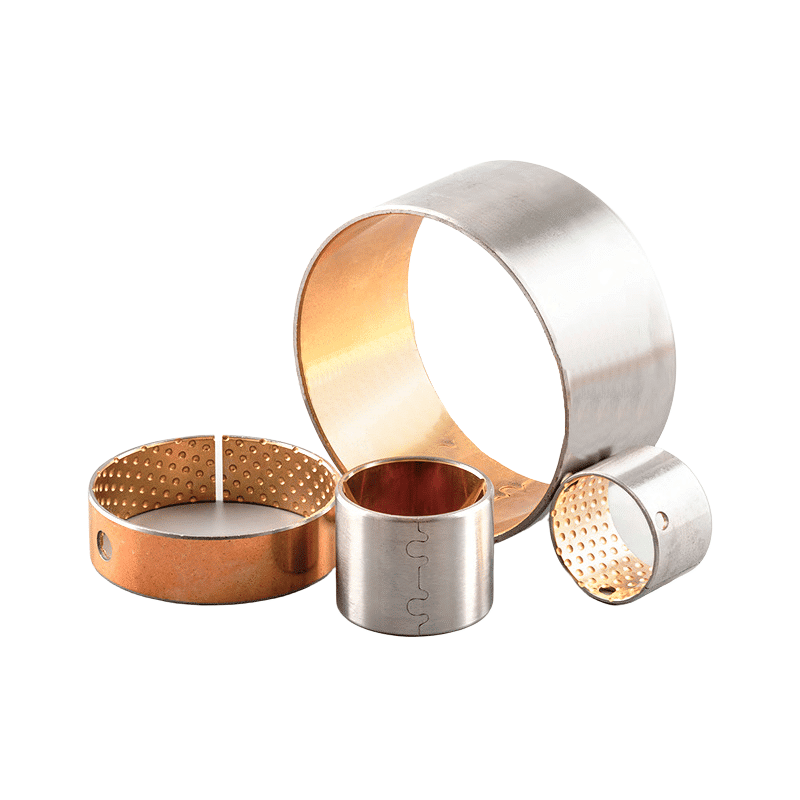
Selection of other composite bushing material of self lubricating bearing that we have manufactured.
Wrapped Bronze Sleeve Bearing, Are you interested in our products?
Manufacturer of bimetal and steel bronze bushing parts according to client’s drawing.