metal powder pressing
metal powder pressing
Say goodbye to the hassle of frequent lubrication maintenance. Our self-lubricating technology ensures smooth operation and reduces wear and tear, extending the lifespan of your equipment. Experience uninterrupted productivity and cost savings as you bid farewell to the need for messy lubricants and time-consuming upkeep.
Manufacturing on Demand, alternative solutions
metal powder pressing
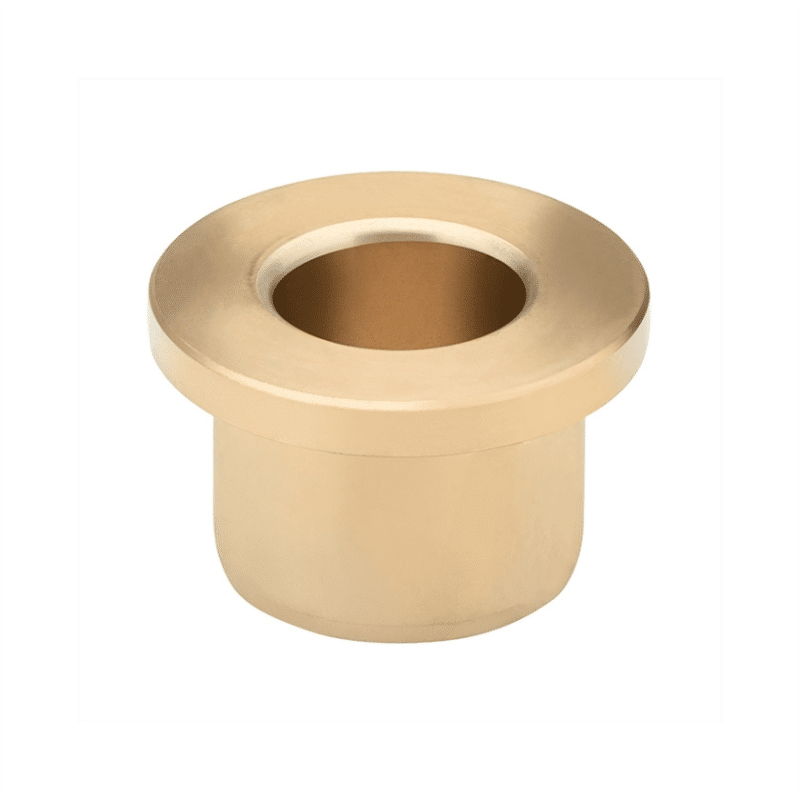
Metal Powder Pressing, Oil Impregnated Bronze Bearings, Powdered Metal Bearings, Metal Powder pressing Find supplier, processes & material
Metal powder pressing is a metal processing technique where a powder is compressed uniaxially between two presses to form a “green body,” which is an unsintered powder compact. This pressing is usually performed at room temperature and is a critical step in the powder metallurgy process, which typically includes powder blending, die compaction, and sintering. The pressing process, particularly with machines like the SACMI MPH presses, is designed for high-speed cycles and continuous work shifts, offering flexibility during tooling and setup stages. The end result is a solid part that is then ready for further processing, such as sintering, to achieve its final properties and strengt!
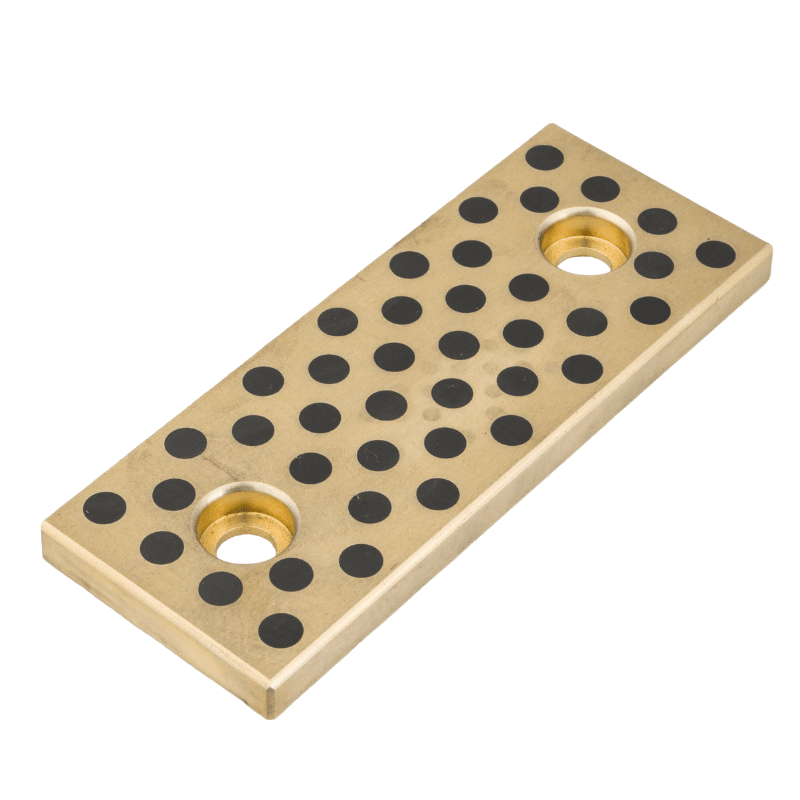
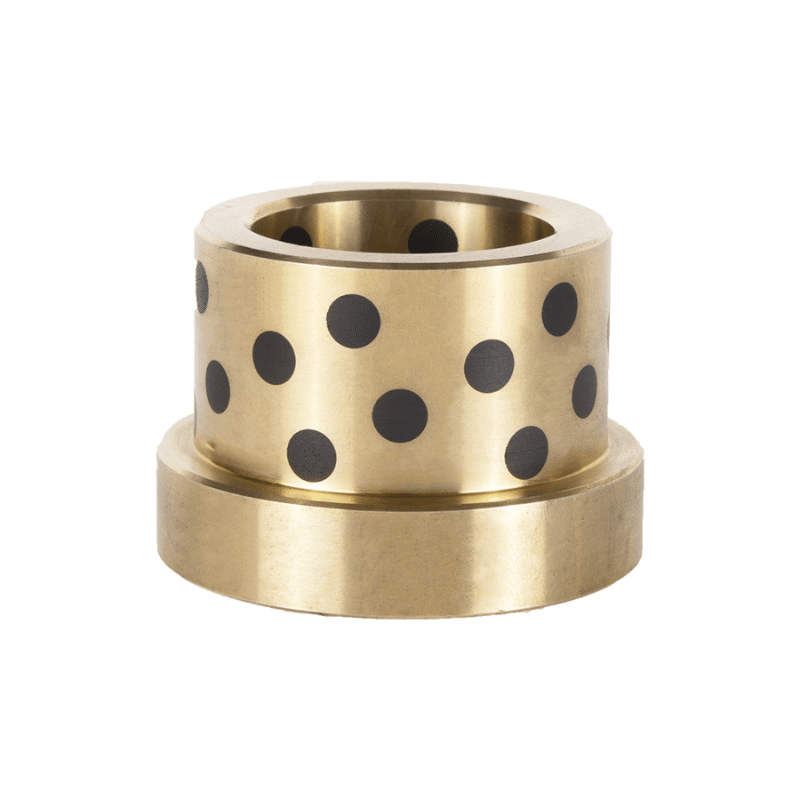
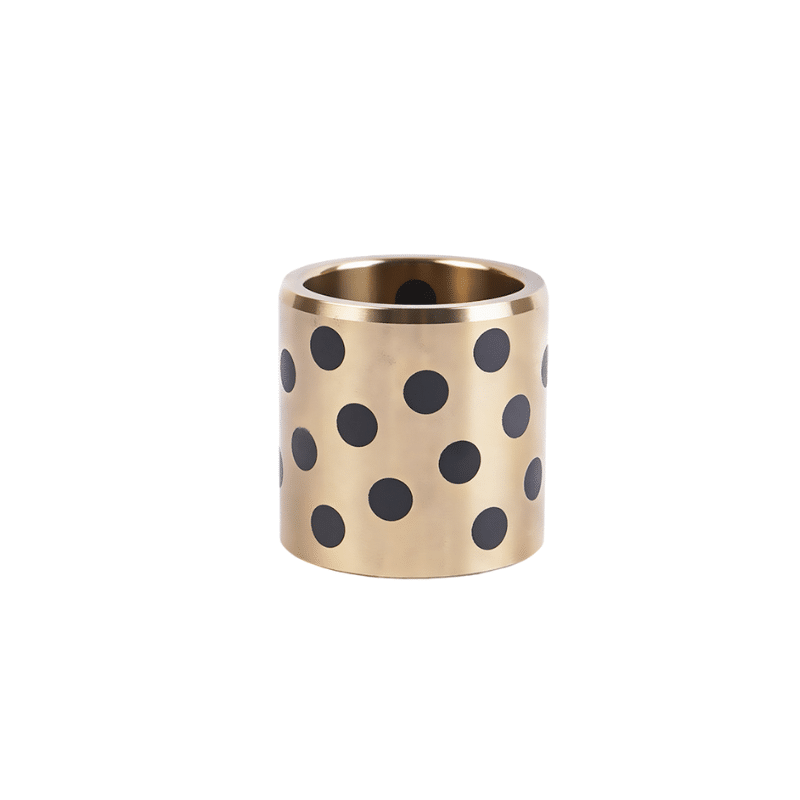
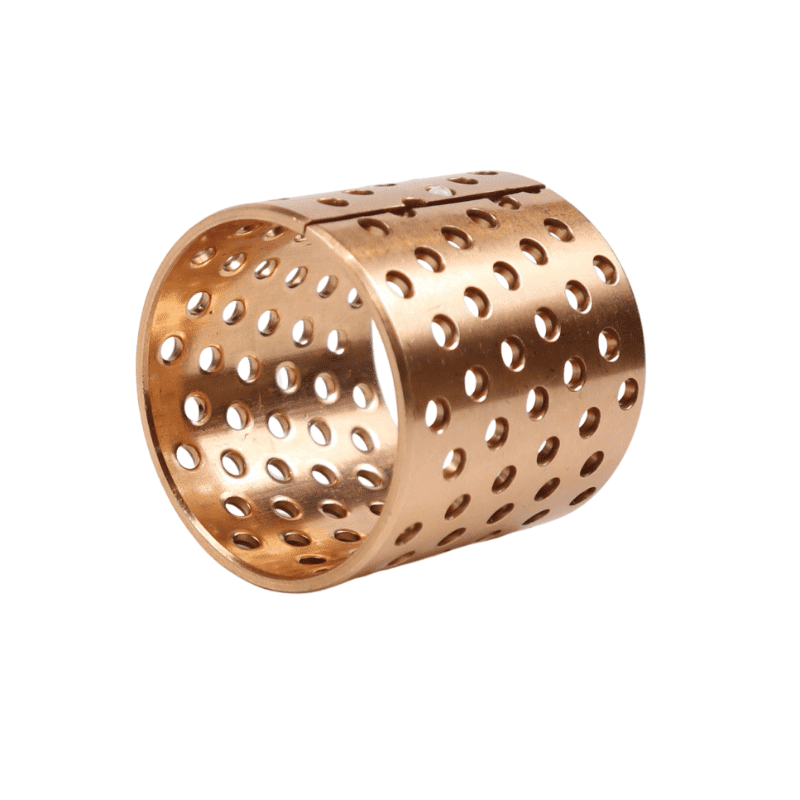
Various manufacturers supply oil-impregnated bronze bearings and powdered metal bearings. VIIPLUS delivers high-quality bronze items, including oil-impregnated bushings, and offers flanged oil-impregnated bronze bushings that meet ASTM standards. Additionally, VIIPLUS provides oil-filled sleeve bronze bushings crafted from self-lubricating powdered metal bronze, ideal for applications requiring wear resistance.
Moreover, Bronze Bushings specializes in standard-sized eco oil-impregnated bronze bearings, designed for use in food service environments. These bearings are self-lubricating and maintenance-free, produced using advanced powdered metallurgy techniques.
Supplier of Oil-impregnated Bronze Bearings and Powdered Metal Bearings, Offering Bronze Powdered Metal Material (Oil Impregnated).
Powder Metallurgy: What Is It? Processes, Bronze Bushing Parts, Metals Used
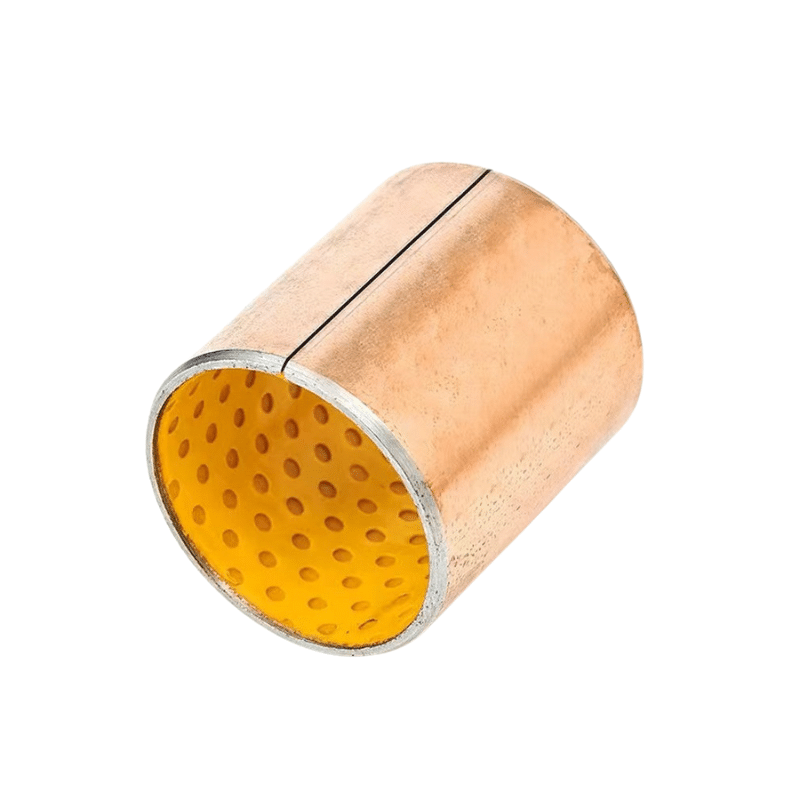
Metal Powder Pressing, Oil-impregnated Bronze Bearings, Powdered Metal Bearings The process of metal powder pressing, specifically for powdered metal (oil-impregnated) components, involves powder metallurgy techniques. Powder metallurgy parts can be impregnated with oil or plastic due to their porosity, offering benefits like self-lubrication and wear resistance
MATERIAL BRONZE POWDERED METAL (OIL IMPREGNATED),
Oil impregnated bronze bushings, Powder metallurgy types & application
Metal powder pressing is a process where a powder is uniaxially compressed between two presses to form a green body. This technique is a fundamental step in manufacturing oil-impregnated bronze bearings, which are a type of powdered metal bearing. Oil-impregnated bronze bearings are manufactured using the powdered metal process, where bronze powder is compressed and then impregnated with oil to enhance lubrication properties. These bearings are designed to maintain lubrication over extended periods, reducing the need for additional lubrication maintenance and offering a longer service life compared to non-impregnated bearings。
Oil-impregnated bronze bearings, made from bronze powdered metal, begin their production journey through a pressing process, which is often the stage where the initial significant challenges of powdered metallurgy (P/M) arise. This process involves shaping the powder into desired forms, a crucial phase known as compacting or pressing.
Compacting or pressing is categorized into two main methods:
- Hot Pressing: This involves compacting powder at high temperatures, typically integrating compaction and sintering simultaneously. It’s a method often reserved for specific applications, such as manufacturing carbide-cutting tools.
- Cold Pressing: This method can be subdivided further into:
- Axial Pressing (Conventional Pressing): A standard method of pressing.
- Isostatic Pressing: A technique where pressure is applied evenly from all directions to the metal powders.
Cold pressing involves exerting pressure on a column of loosely packed metal powders within a closed die to create a green compact, a preliminary shaped part before sintering. This technique is prevalent in P/M, responsible for producing the majority of parts.
During the pressing process, metal powders do not behave like liquids; they don’t transmit pressure uniformly in all directions when compressed in a die. The flow of the powders and the resulting compaction are influenced by various factors, including the powder’s characteristics such as particle size, shape, and composition.
Achieving uniform density throughout the compact is crucial for dimensional consistency during subsequent sintering. The required pressure for compaction varies with the type of metal powder, and excessive pressure can lead to issues like fractures in the compacted part.
Post-sintering, a sizing or repressing operation might be necessary to achieve precise dimensions, especially for parts where high accuracy is essential. This step involves repressing the part to adjust dimensions altered during sintering.
The compacting process in P/M involves feeding powder into a die, compacting it into shape by applying pressure, and then extracting the formed part. Early presses, adapted from pharmaceutical and small stamping presses, lacked the necessary rigidity and adjustability, limiting the quality and complexity of producible parts.
Modern pressing equipment, available in various tonnages and designs, offers enhanced rigidity and accuracy. The majority of P/M parts are compacted mechanically, with mechanical presses preferred for lower pressure ranges due to their speed advantage over hydraulic presses. The selection between mechanical and hydraulic presses largely depends on the required energy source for compaction.
Metal powder pressing is a key process in the field of powder metallurgy, where a powder is compressed uniaxially between two presses to form a green body. This method is fundamental for creating precision and highly accurate parts by pressing powdered metals and alloys into a rigid die under pressure. The process encompasses powder mixing, compacting, and sintering, where the compacted powder is heated to a temperature below its melting point to fuse the particles into a solid piece. This technique allows the production of complex shapes that are challenging to achieve with traditional metalworking methods!
Your expert in self-lubricating Bearing
and Bronze alloys – serving globally
Brand replacement products and functionally equivalent parts, alternative solutions
Manufactures flange bronze bearings, service & maintenance companies to meet the exacting specifications required in a wide range of industrial applications.
Machined bronze bushing that meet the exacting requirements & specifications supplied by our clients. Spherical bearings, spindles, semi-spheres and supports that we have manufactured.
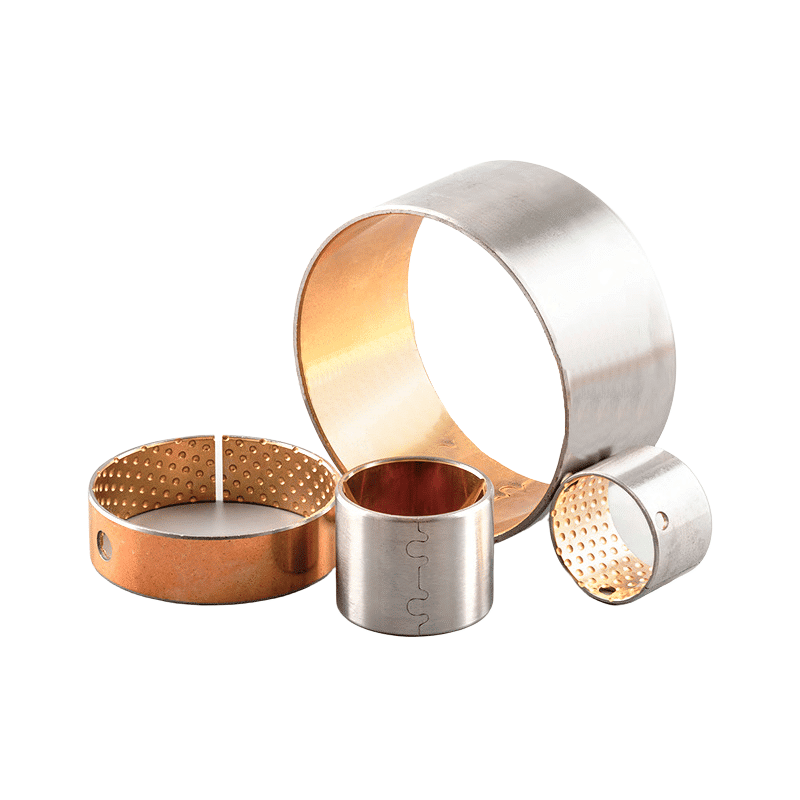
You will find to follow a selection of self lubricating bronze bearing material CuSn7Zn4Pb7, CuSn12, CuAl10Fe5Ni5,
CuZn25Al5Mn4Fe3
Alternative solution,We offer an outsourced machining service for bronze bushes, manufacturing precise parts to the designs supplied to us by our clients.
Selection of other composite bushing material of self lubricating bearing that we have manufactured.
Wrapped Bronze Sleeve Bearing, Are you interested in our products?
Manufacturer of bimetal and steel bronze bushing parts according to client’s drawing.