How to Calculate Propeller Torque for PB2 Bronze Bearing and C63000 Aluminum Bronze Bearing
Bearings and Bushings for the Future: Precision and Customization: Our company, in bearing engineering with decades of experience, designs and develops high-precision self-lubricating bronze bearings & plain bushes. We offer a wide array of sliding bearings tailored to meet specific needs. Renowned for our expertise in custom bronze bushing and slide plate solutions, we provide an expansive selection of bushing metal alloys. Contact us today to benefit from unparalleled services at competitive prices.
How to Calculate Propeller Torque for PB2 Bronze Bearing and C63000 Aluminum Bronze Bearing
Excellence in the manufacturing process
How to Calculate Propeller Torque for PB2 Bronze Bearing and C63000 Aluminum Bronze Bearing
The torque generated by a propeller in a marine vessel plays a crucial role in ensuring the vessel’s performance and efficiency. Accurate calculation of this torque is essential for designing and selecting appropriate bearing materials to withstand the mechanical stresses placed on the propeller hub during operation. PB2 bronze and C63000 aluminum bronze are two commonly used materials for bearings in marine applications, each offering unique advantages. In this guide, we will explore how to calculate propeller torque for these two bearing materials.
Understanding Propeller Torque
Propeller torque refers to the rotational force exerted by the propeller on the bearing, typically measured in Newton-meters (Nm). The torque is crucial for determining the stress experienced by the bearing materials and ensuring that the system operates smoothly without premature wear or failure.
Factors Affecting Propeller Torque
Several factors influence the torque generated by a marine vessel’s propeller:
- Propeller Diameter and Pitch: Larger and more aggressive propellers generate more torque.
- Engine Power and RPM: Higher engine power and revolutions per minute (RPM) result in greater torque.
- Water Resistance: Increased resistance (e.g., from rough seas or heavy loads) leads to higher torque.
- Bearing Material Properties: The type of material used for the bearing affects its ability to withstand the torque and provide smooth rotation.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Torque for Propeller Hub Bearings
- Determine the Power Delivered by the Engine The torque generated by the propeller is directly related to the engine’s power output. First, calculate the power being transmitted from the engine to the propeller. The formula for power is:P=T×ωP = T times omega
Where:
- PP = Power (in Watts)
- TT = Torque (in Newton-meters)
- ωomega = Angular velocity (in radians per second)
Angular velocity is related to the engine RPM by the following formula:
ω=2π×RPM/60omega = 2 pi times text{RPM} / 60
- Calculate the Torque Rearranging the equation for power, we can solve for torque:T=P/ωT = P / omega
This will give the torque generated by the propeller.
- Consider the Bearing Material Properties The bearing material affects how much load it can handle and its ability to transmit torque effectively. Both PB2 bronze and C63000 aluminum bronze offer excellent mechanical properties for bearing applications, but they differ in their characteristics:
- PB2 Bronze (commonly known as Phosphor Bronze) is known for its excellent wear resistance and low friction. It’s ideal for applications where durability and corrosion resistance are key factors.
- C63000 Aluminum Bronze offers higher strength and excellent resistance to corrosion in seawater environments, making it particularly suitable for high-load applications.
While both materials can handle significant torque, C63000 aluminum bronze is typically more robust and better suited for high-load or high-torque applications due to its strength.
- Assess the Load Distribution The torque load on the bearings is distributed based on the geometry of the propeller hub and bearing design. Proper load distribution ensures that the bearing does not experience excessive stress, which could lead to premature wear or failure.
- Calculate the Bearing Load The bearing load can be estimated using the formula:F=T/rF = T / r
Where:
- FF = Bearing load (in Newtons)
- TT = Torque (in Newton-meters)
- rr = Radius of the bearing or propeller hub (in meters)
This load can then be compared to the material’s maximum allowable load to ensure the bearing will perform optimally without failure.
Mechanical Properties of PB2 Bronze and C63000 Aluminum Bronze
Both PB2 bronze and C63000 aluminum bronze possess distinct advantages in terms of mechanical properties, which affect how they handle torque in propeller applications:
- PB2 Bronze:
- Tensile Strength: 550-750 MPa
- Hardness: 80-150 HB
- Wear Resistance: Excellent, particularly when lubricated
- Corrosion Resistance: Good, particularly in freshwater and mild seawater conditions
- C63000 Aluminum Bronze:
- Tensile Strength: 900-1100 MPa
- Hardness: 180-220 HB
- Wear Resistance: Excellent, particularly in harsh marine environments
- Corrosion Resistance: Outstanding, especially in seawater and harsh marine conditions
C63000 aluminum bronze has higher tensile strength and hardness, making it more suited for high-torque applications where greater strength is needed to resist deformation.
Torque Load on Bearings
In marine applications, the torque load placed on bearings like PB2 bronze and C63000 aluminum bronze can vary significantly depending on operational conditions such as speed, load, and environmental factors. The torque load can be more accurately determined by factoring in the propeller’s operational RPM, diameter, and pitch.
Best Practices for Calculating Propeller Torque
- Consider Operating Conditions: Factor in real-world conditions such as sea state, load variations, and engine performance.
- Choose the Right Bearing Material: PB2 bronze is ideal for moderate torque and corrosion resistance, while C63000 aluminum bronze is better suited for high-torque, high-stress environments.
- Monitor Wear and Performance: Regular monitoring of the bearing’s performance under load will ensure that torque levels are within acceptable limits and that bearing degradation is detected early.
Conclusion
When calculating propeller torque for marine vessel propeller hub bearings, it is crucial to consider the mechanical properties of the bearing materials, as well as the operational parameters of the vessel. PB2 bronze offers excellent wear resistance, making it ideal for less demanding applications, while C63000 aluminum bronze is more suited for high-torque environments due to its superior strength and corrosion resistance.
By following the steps outlined above and understanding the influence of bearing material properties on torque transmission, engineers can ensure the longevity and efficiency of marine propeller systems, improving both performance and safety.
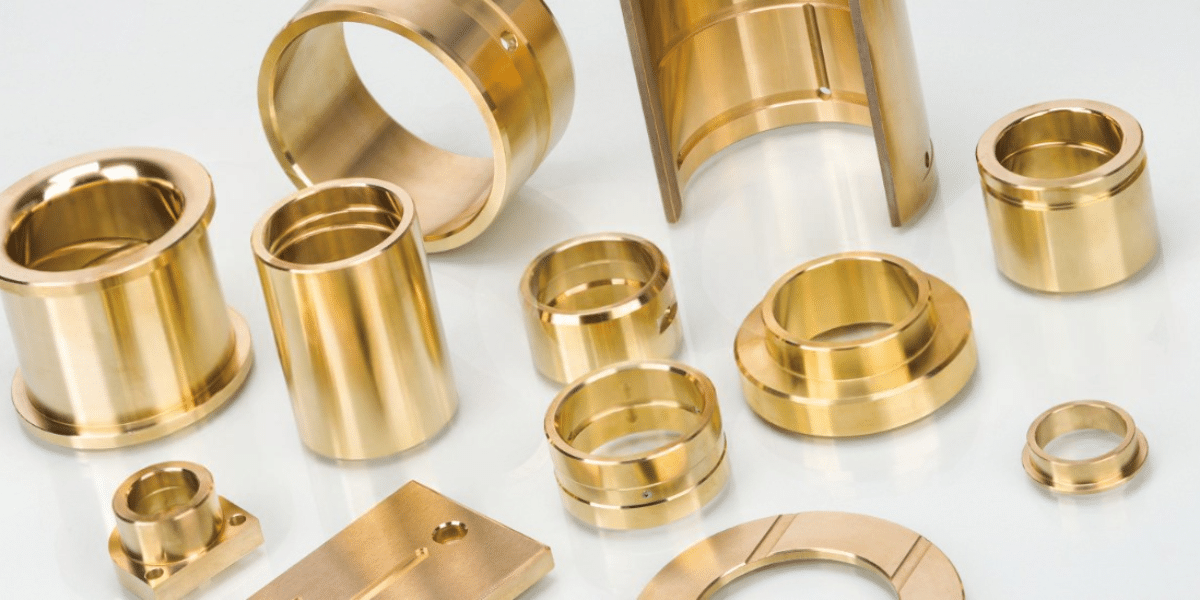
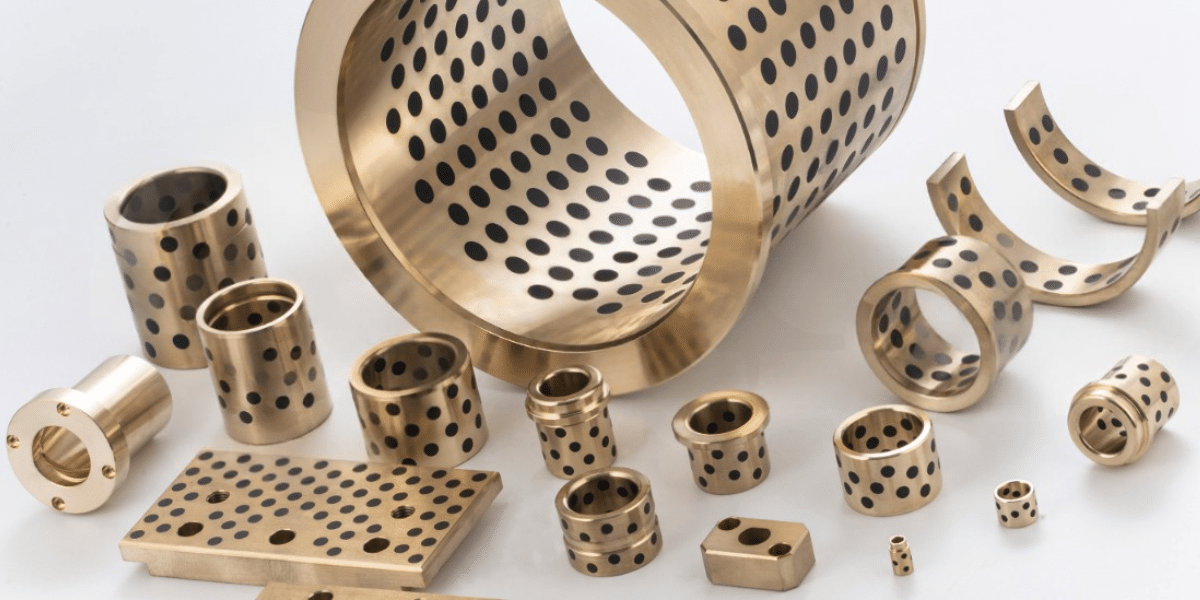


PB2 Bronze & C63000 Aluminum Bronze Composition
PB2 Bronze: PB2 bronze is primarily a phosphor bronze alloy, composed of the following elements:
- Copper (Cu): ~90%
- Tin (Sn): ~10%
- Phosphorus (P): Trace amounts
C63000 Aluminum Bronze: C63000 is an aluminum bronze alloy with the following composition:
- Copper (Cu): ~82%
- Aluminum (Al): ~10%
- Nickel (Ni): ~5%
- Iron (Fe): ~3%
Key Characteristics
PB2 Bronze:
- Corrosion Resistance: Excellent, especially in marine and acidic environments.
- Wear Resistance: Good, with low friction, making it ideal for bearings and bushings.
- Fatigue Resistance: High, making it suitable for dynamic applications.
- Strength: Lower compared to C63000 aluminum bronze.
C63000 Aluminum Bronze:
- Strength and Hardness: Exceptional, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
- Wear and Galling Resistance: Excellent, ideal for high-load, high-speed operations.
- Corrosion Resistance: Superior, particularly in seawater and aggressive chemical environments.
- Thermal Conductivity: Higher than PB2 bronze, beneficial for heat dissipation in demanding applications.
Applications
PB2 Bronze:
- Bearings and bushings for moderate loads.
- Gears, springs, and fasteners.
- Marine components like propeller shafts and pumps.
- Electrical connectors and springs.
C63000 Aluminum Bronze:
- Heavy-duty bearings and bushings.
- Gears, valves, and pump components.
- Marine hardware, including propellers and shafts.
- High-stress industrial applications, such as turbines and high-performance machinery.
Torque Capacity
C63000 aluminum bronze boasts a significantly higher torque capacity than PB2 bronze, due to its superior shear strength. This makes C63000 ideal for applications with higher torque or extreme loading conditions.
Cost and Availability
PB2 Bronze:
- Cost: Generally more affordable than aluminum bronze.
- Availability: Widely available for standard bearing and bushings applications.
C63000 Aluminum Bronze:
- Cost: More expensive, primarily due to the higher content of aluminum and nickel.
- Availability: Preferred for specialized, high-performance applications, making it less common than PB2 bronze.
Selection Criteria
Choose PB2 Bronze if:
- The application requires moderate strength and wear resistance.
- Cost is a critical factor.
- The environment involves corrosion, particularly in marine applications.
Choose C63000 Aluminum Bronze if:
- The application involves high loads, high speeds, or heavy wear.
- Superior strength and durability are essential.
- The environment is highly corrosive (e.g., seawater, chemicals) or involves high-temperature conditions.
Final Recommendation
For a torque requirement of 350 Nm, both PB2 and C63000 aluminum bronze are suitable. However:
- C63000 Aluminum Bronze is capable of handling the torque with a higher safety margin, though it might be considered overkill for this specific application.
- PB2 Bronze is more cost-effective and sufficient for this level of torque, making it the practical choice for moderate applications.
If the application involves higher loads, harsh environments, or dynamic stresses, C63000 Aluminum Bronze is the better choice. For moderate torque and general use, PB2 Bronze is a cost-efficient and reliable option.

Solutions For Every Industry
Searching for Dependable Bushing Solutions? viiplus Has What You Need.

Design Guides, Materials
Bushing design, Comprehensive design manuals covering a range of self-lubricating materials used in all of viiplus’s manufacturing processes.

Technical Guides
Manufacturing On Demand, Technical Guides For Machining Design. Discover the latest in metal alloys, materials, and design tips for manufacturing custom machined and self-lubricating bearing parts.

Get Instant Quote
To receive your instant quote, simply upload your drawing file and choose your production process & bushing material.
Prototyping, Place Order
After you place your order, we will start the production process. You will receive updates when your order has completed production and is ready to be dispatched.

Receive Your custom Parts
We provide precision-inspected high-quality parts, packing lists and documents, and delivery tracking.

