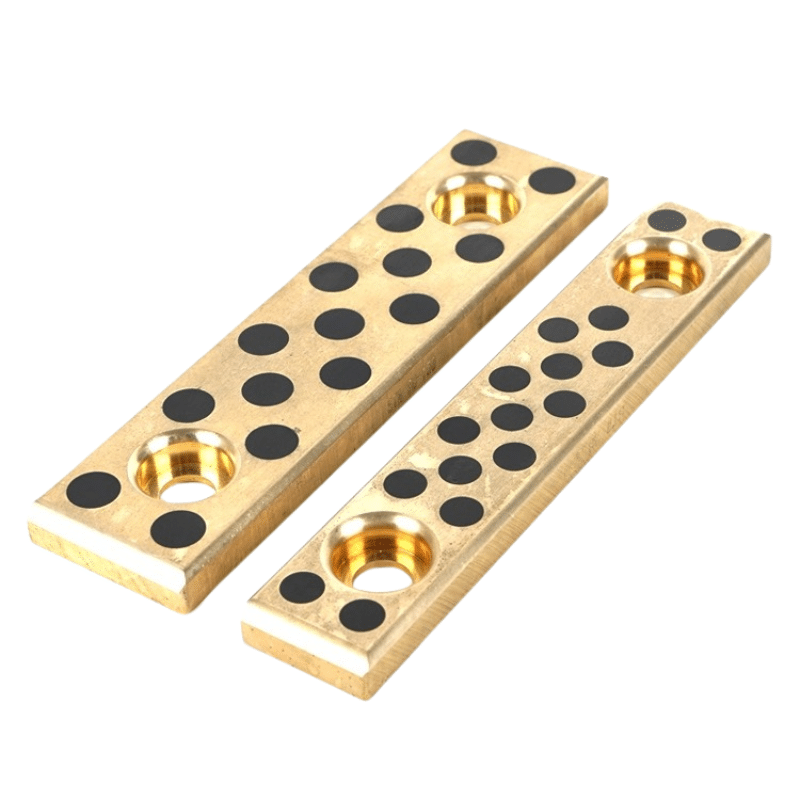
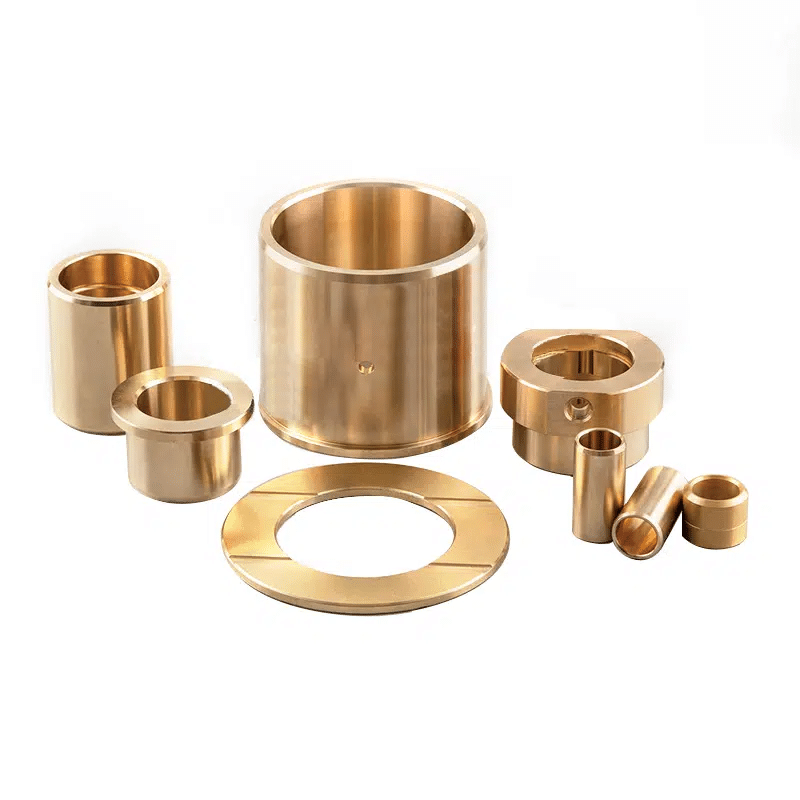
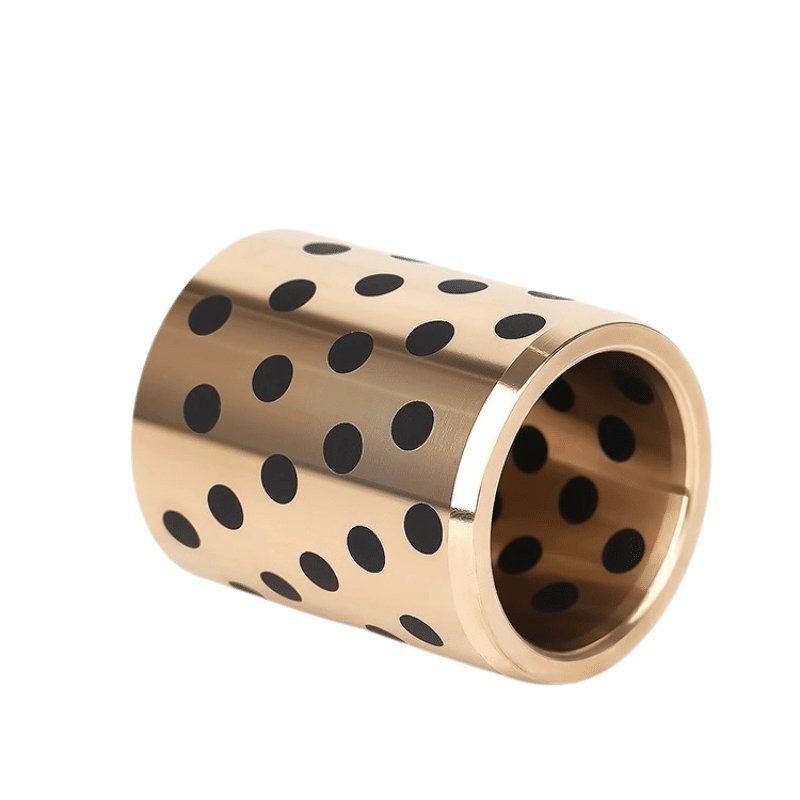
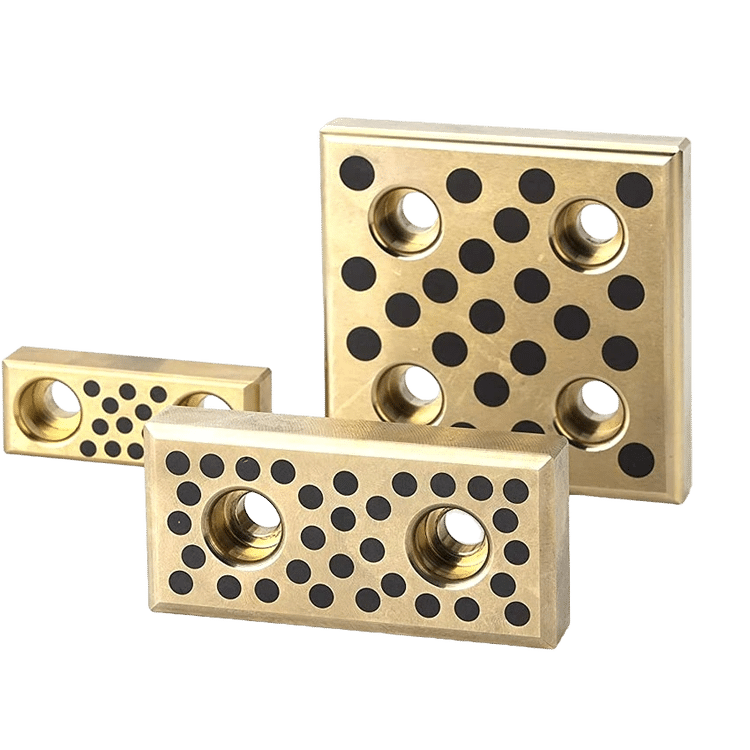
What’s the Difference Between Mold Dies?
Bearings and Bushings for the Future: Precision and Customization: Our company, in bearing engineering with decades of experience, designs and develops high-precision self-lubricating bronze bearings & plain bushes. We offer a wide array of sliding bearings tailored to meet specific needs. Renowned for our expertise in custom bronze bushing and slide plate solutions, we provide an expansive selection of bushing metal alloys. Contact us today to benefit from unparalleled services at competitive prices.
What’s the Difference Between Mold Dies?
Explore Other Alloys, Suggested Searches: Copper Brass Bronze Copper Nickel
Bearing Bushing, Search Our Material Alloy
Providing Brass, Bronze, and Specialty Copper Alloys, Copper Alloy Machining Services

Solutions For Every Industry
Searching for Dependable Bushing Solutions? viiplus Has What You Need.

Design Guides, Materials
Bushing design, Comprehensive design manuals covering a range of self-lubricating materials used in all of viiplus’s manufacturing processes.

Technical Guides
Manufacturing On Demand, Technical Guides For Machining Design. Discover the latest in metal alloys, materials, and design tips for manufacturing custom machined and self-lubricating bearing parts.

Get Instant Quote
To receive your instant quote, simply upload your drawing file and choose your production process & bushing material.
Prototyping, Place Order
After you place your order, we will start the production process. You will receive updates when your order has completed production and is ready to be dispatched.

Receive Your custom Parts
We provide precision-inspected high-quality parts, packing lists and documents, and delivery tracking.






